| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
| 29 | 30 | 31 |
- react-router-dom
- 코드업
- react
- Servlet
- TypeScript
- 그럼에도불구하고
- 변수
- 자바
- github
- CSS
- 그럼에도 불구하고
- coding
- JS
- redux
- HTML
- max-width
- java
- 반응형 페이지
- JavaScript
- node.js
- git
- 코딩테스트
- media query
- 프론트엔드
- node
- webpack
- cleancode
- 자바문제풀이
- @media
- frontend
- Today
- Total
그럼에도 불구하고
[React] Components와 Props란? 본문
오늘은 props에 대해 알아보겠습니다.
React에서는 component를 통해 UI를 재사용 가능한 개별적인 여러 조각으로 나누고, 각 조각을 개별적으로 살펴볼 수 있습니다.
개념적으로 컴포넌트는 JavaScript 함수와 유사합니다. "props"라고 하는 임의의 입력을 받은 후, 화면에 어떻게 표시되는지를 기술하는 react element를 반환합니다.
[ 함수 컴포넌트 ( Function Component ) ]
component를 정의하는 가장 간단한 방법은 JavaScript 함수를 작성하는 것입니다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | import './ExpenseItem.css'; function ExpenseItem(props) { return ( <div className='expense-item'> <div>{props.date.toISOString()}</div> <div className='expense-item__description'> <h2>{props.title}</h2> <div className='expense-item__price'>${props.amount}</div> </div> </div> ); } export default ExpenseItem; | cs |
이 함수는 데이터를 가진 하나의 "props" (props는 속성을 나타내는 데이터입니다.) 객체 인자를 받은 후 react element를 반환하므로 유효한 React component 입니다. 이러한 component는 JavaScript 함수이기 때문에 말 그대로 “함수 컴포넌트”라고 호칭합니다.
[ 컴포넌트 렌더링 ]
React element는 사용자 정의 component로 나타낼 수 있습니다.
1 | <ExpenseItem title={expenses[0].title} amount={expenses[0].amount} date={expenses[0].date}></ExpenseItem> | cs |
React가 사용자 정의 component로 작성한 element를 발견하면 JSX 어트리뷰트와 자식을 해당 컴포넌트에 단일 객체로 전달합니다. 이 객체를 “props”라고 합니다.
다음은 페이지에서 expenses 배열안에 있는 객체들을 렌더링 하는 예시입니다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 | import ExpenseItem from "./components/ExpenseItem"; function App() { const expenses = [ { id: 'e1', title: 'Toilet Paper', amount: 94.12, date: new Date(2020, 7, 14), }, { id: 'e2', title: 'New TV', amount: 799.49, date: new Date(2021, 2, 12) }, { id: 'e3', title: 'Car Insurance', amount: 294.67, date: new Date(2021, 2, 28), }, { id: 'e4', title: 'New Desk (Wooden)', amount: 450, date: new Date(2021, 5, 12), }, ]; return ( <div> <h2>Let`s get started!</h2> <ExpenseItem title={expenses[0].title} amount={expenses[0].amount} date={expenses[0].date}></ExpenseItem> </div> ); } export default App; | cs |
※ 컴포넌트의 이름은 항상 대문자로 시작합니다.
React는 소문자로 시작하는 컴포넌트를 DOM 태그로 처리합니다. 예를 들어 <div />는 HTML div 태그를 나타내지만, <Welcome />은 컴포넌트를 나타내며 범위 안에 Welcome이 있어야 합니다.
[ 컴포넌트 합성 ]
컴포넌트는 자신의 출력에 다른 컴포넌트를 참조할 수 있습니다. 이는 모든 세부 단계에서 동일한 추상 컴포넌트를 사용할 수 있음을 의미합니다. React 앱에서는 버튼, 폼, 다이얼로그, 화면 등의 모든 것들이 흔히 컴포넌트로 표현됩니다.
예를 들어 ExpenseItem을 여러 번 렌더링 하게 만들 수 있습니다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 | import ExpenseItem from "./components/ExpenseItem"; function App() { const expenses = [ { id: 'e1', title: 'Toilet Paper', amount: 94.12, date: new Date(2020, 7, 14), }, { id: 'e2', title: 'New TV', amount: 799.49, date: new Date(2021, 2, 12) }, { id: 'e3', title: 'Car Insurance', amount: 294.67, date: new Date(2021, 2, 28), }, { id: 'e4', title: 'New Desk (Wooden)', amount: 450, date: new Date(2021, 5, 12), }, ]; return ( <div> <h2>Let`s get started!</h2> <ExpenseItem title={expenses[0].title} amount={expenses[0].amount} date={expenses[0].date}></ExpenseItem> <ExpenseItem title={expenses[1].title} amount={expenses[1].amount} date={expenses[1].date}></ExpenseItem> <ExpenseItem title={expenses[2].title} amount={expenses[2].amount} date={expenses[2].date}></ExpenseItem> <ExpenseItem title={expenses[3].title} amount={expenses[3].amount} date={expenses[3].date}></ExpenseItem> </div> ); } export default App; | cs |
일반적으로 새 React 앱은 최상위에 단일 App Component를 가지고 있습니다. 하지만 기존 앱에 React를 통합하는 경우에는 Button과 같은 작은 컴포넌트부터 시작해서 뷰 계층의 상단으로 올라가면서 점진적으로 작업해야 할 수 있습니다.
[ 컴포넌트 추출 ]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 | import './ExpenseItem.css'; function ExpenseItem(props) { const month = props.date.toLocaleString('en-US', {month:'long'}); const day = props.date.toLocaleString('en-US', {day:'2-digit'}); const year = props.date.getFullYear(); return ( <div className='expense-item'> <div className='expense-date'> <div className='expense-date__month'>{month}</div> <div className='expense-date__year'>{year}</div> <div className='expense-date__day'>{day}</div> </div> <div className='expense-item__description'> <h2>{props.title}</h2> <div className='expense-item__price'>${props.amount}</div> </div> </div> ); } export default ExpenseItem; | cs |
위의 코드에서 expense-date는 날짜를 나타내기 위한 요소입니다.
이 요소를 기존 컴포넌트에서 추출해 보겠습니다.
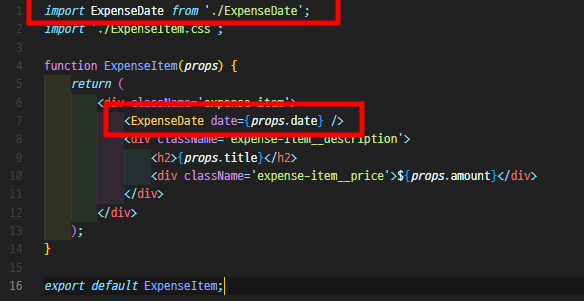
ExpenseDate라는 명의 Component를 추출하고 위에서 ExpenseDate 파일에 있는 ExpenseDate 함수를 import 한 상태입니다.
ExpenseDate.js을 확인해 보겠습니다.
ExpenseDate.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 | import './ExpenseDate.css'; function ExpenseDate(props) { const month = props.date.toLocaleString('en-US', {month:'long'}); const day = props.date.toLocaleString('en-US', {day:'2-digit'}); const year = props.date.getFullYear(); return ( <div className='expense-date'> <div className='expense-date__month'>{month}</div> <div className='expense-date__year'>{year}</div> <div className='expense-date__day'>{day}</div> </div> ); } export default ExpenseDate; | cs |
다음과 같이 날짜를 구하기 위한 모든 요소를 추출해 온 상태입니다.
이렇게 하면 Component를 추출하여 사용할 수 있으며, 이는 재사용 가능한 Component를 만들어 놓는 것이기 때문에 크기가 큰 파일일수록 작업할 때 두각을 나타냅니다. 또한, UI 일부가 여러 번 사용되거나, UI 일부가 자체적으로 복잡한 경우에는 별도의 컴포넌트로 만드는 것이 좋습니다.
※ props는 읽기 전용이다!?
함수 컴포넌트의 자체 props를 수정해서는 안됩니다. 다음 sum 함수를 살펴봅시다.
1 2 3 | function sum(a, b) { return a + b; } | cs |
이런 함수들은 순수 함수라고 호칭합니다. 입력값을 바꾸려 하지 않고 항상 동일한 입력값에 대해 동일한 결과를 반환하기 때문입니다.
반면에 다음 함수는 자신의 입력값을 변경하기 때문에 순수 함수가 아닙니다.
1 2 3 | function withdraw(account, amount) { account.total -= amount; } | cs |
React는 매우 유연하지만 한 가지 엄격한 규칙이 있습니다.
모든 React 컴포넌트는 자신의 props를 다룰 때 반드시 순수 함수처럼 동작해야 한다는 것입니다.
'React > React basics' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [React] Portal이란? (0) | 2023.04.06 |
|---|---|
| [React] htmlFor란? (0) | 2023.04.06 |
| [React] Styled Component란? (0) | 2023.04.04 |
| [React] state란? (0) | 2023.03.29 |
| [React] React란? (0) | 2023.03.17 |

